Electrochemistry
- Determine No. Of Stereoisomers
← Back to Intro to Org Chem no. of stereoisomers = 2n n = no. of stereogenic centers i.e. chiral C + C=C or cyclic rings that can exhibit cis/trans Students make mistakes when they blindly count the total number of C=C...
- Chemical Bonding
NOTES: TYPES OF QUESTIONS: Determine Structure and Bonding Draw Dot-Cross Diagrams Determine Type of Bonding for Simple Molecules Predict/ Account for Physical Properties ...
- H2 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- H1 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry : 12.5 Organic Reaction
TYPE OF CLEAVAGE : 2 type of bond cleavage:- Hemolytic cleavageHeterolytic cleavage Hemolytic cleavage The breaking of a single (two-electron) bond in which one electron remains on each of the atoms. Also known as free-radical reaction; homolysis. ...
Electrochemistry
Determine no. of Structural Isomers
← Back to Intro to Org Chem
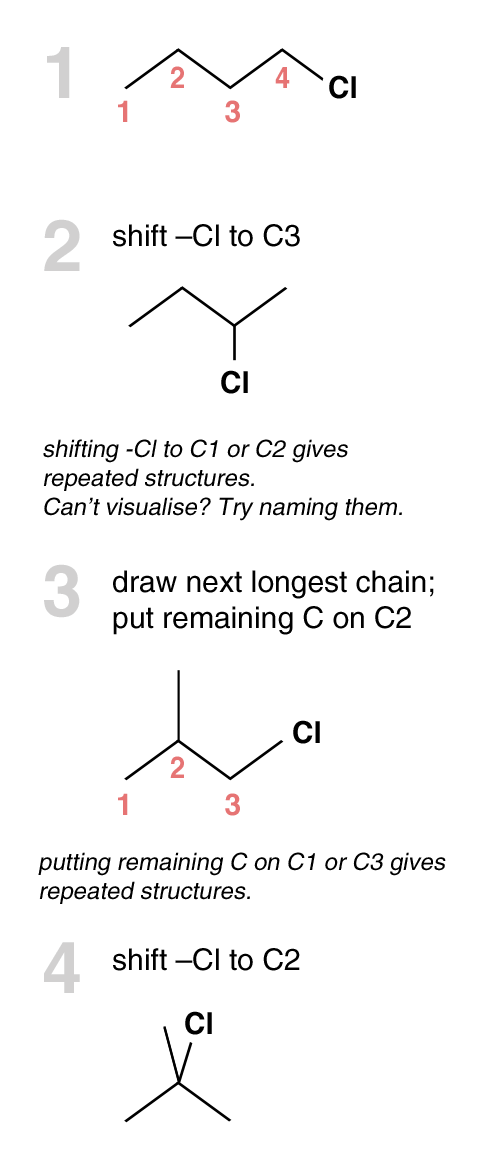
[Bad News] There is no mathematical formula available to calculate the number of structural isomers. You have to draw out all possible structures.
[Good News] There is a general approach for that.
| APPROACH
|
Example : Determine the number of structural isomers for C4H10Cl.

There are 4 structural isomers for C4H10Cl.
- Determine No. Of Stereoisomers
← Back to Intro to Org Chem no. of stereoisomers = 2n n = no. of stereogenic centers i.e. chiral C + C=C or cyclic rings that can exhibit cis/trans Students make mistakes when they blindly count the total number of C=C...
- Chemical Bonding
NOTES: TYPES OF QUESTIONS: Determine Structure and Bonding Draw Dot-Cross Diagrams Determine Type of Bonding for Simple Molecules Predict/ Account for Physical Properties ...
- H2 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- H1 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry : 12.5 Organic Reaction
TYPE OF CLEAVAGE : 2 type of bond cleavage:- Hemolytic cleavageHeterolytic cleavage Hemolytic cleavage The breaking of a single (two-electron) bond in which one electron remains on each of the atoms. Also known as free-radical reaction; homolysis. ...
