Electrochemistry
- Determine Type Of Bonding For Simple Molecules
← Back to Chemical Bonding To determine the type of molecule (polar/ non-polar) and IMF, you will need these four steps: 1) Draw dot-cross diagram: 1 Determine the central atom and surrounding atoms. Central...
- How To Draw Dot-cross Diagram
← Back to Chemical Bonding 1 Determine the central atom and surrounding atoms. Central atom is commonly the: - Element with the lesser no. of atoms - First element in chemical formula (except H) - Least electronegative...
- Atomic Structure
Learning Objectives (a) identify and describe protons, neutrons and electrons in terms of their relative charges and relative masses (b) deduce the behaviour of beams of protons, neutrons and electrons in both electric and magnetic fields (c) describe...
- H1 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- Electrochemistry : 10.3 : Electrolysis Cell
VOLTAN CELL VS ELECTRIOLYSIS CELL . Voltaic cell :use a spontaneous reaction to generate electric energy. Electrolysis :use electric energy to drive non- spontaneous energy. VOLTAIC CELL. ELECTROLYTICelectrons generate...
Electrochemistry
Oxidation Number
← Back to Electrochemistry
- Oxidation numbers are arbitrary numbers assigned to atoms to describe their relative state of oxidation or reduction i.e. how oxidised or reduced they are.
- They are assigned according to an arbitrary set of rules:
| Species | Oxidation No. (ON) | Example: Species (ON) |
| Free Elements | = Zero | Mg (0), Cl2 (0), S8 (0) |
| Monoatomic Ions | = Charge on Ion | Ca2+ (+2), O2– (-2) |
| Polyatomic Ions | Sum of ON = Charge on Ion * | SO42– Let the ON of S be x. x + 4(-2) = -2; x = +6 |
| Neutral Compounds/ Molecules | Sum of ON = Zero * | NCl3 Let the ON of N be x. x + 3(-1) = 0; x = +3 |
* requires memorising of the common ON of elements:
| Element | Oxidation No. (ON) |
| Hydrogen (H) | +1 |
| Oxygen (O) | -2 |
| Halogens (X) | -1 |
Practice:
Determine the oxidation numbers of the underlined atoms in the following species:
(a) P4
(b) Cr3+
(c) VO2+
(d) MnO2
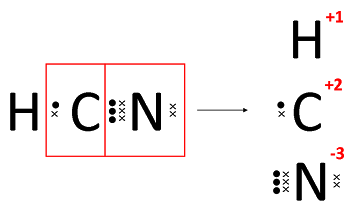
Universal method for determining ON:
- Break all bonds in species
- Assign shared e- to more electro-ve atom
- ON = resultant charge on atom
Example: HCN

Practice:
Determine the oxidation numbers of the elements in carbon disulfide CS2.
- Determine Type Of Bonding For Simple Molecules
← Back to Chemical Bonding To determine the type of molecule (polar/ non-polar) and IMF, you will need these four steps: 1) Draw dot-cross diagram: 1 Determine the central atom and surrounding atoms. Central...
- How To Draw Dot-cross Diagram
← Back to Chemical Bonding 1 Determine the central atom and surrounding atoms. Central atom is commonly the: - Element with the lesser no. of atoms - First element in chemical formula (except H) - Least electronegative...
- Atomic Structure
Learning Objectives (a) identify and describe protons, neutrons and electrons in terms of their relative charges and relative masses (b) deduce the behaviour of beams of protons, neutrons and electrons in both electric and magnetic fields (c) describe...
- H1 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- Electrochemistry : 10.3 : Electrolysis Cell
VOLTAN CELL VS ELECTRIOLYSIS CELL . Voltaic cell :use a spontaneous reaction to generate electric energy. Electrolysis :use electric energy to drive non- spontaneous energy. VOLTAIC CELL. ELECTROLYTICelectrons generate...
