Electrochemistry
- What Is An Activity Series, And How Is It Used?
An activity series is a list of substances ranked in order of relative reactivity. For example, magnesium metal can knock hydrogen ions out of solution, so it is considered more reactive than elemental hydrogen: Mg(s) + 2 H+(aq) H2(g) + Mg2+(aq) Zinc...
- Predict/ Account For Physical Properties
← Back to Chemical Bonding Approach: Determine the type of substance (metal/ ionic/ covalent) and structure (giant metallic/ giant ionic/ giant covalent/ simple molecular) Determine bonding relevant to property Focus on that particular column...
- Chemical Bonding
Overview * Covalent bonds are also present in simple molecular structures. However, they are not broken during physical reactions (e.g. boiling, melting) For questions related to Chemical Bonding: Determine the type of substance (metal/...
- O-level Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
1. Experimental Chemistry • Experimental design • Methods of purification and analysis • Identification of ions and gases 2. The Particulate Nature of Matter • Kinetic particle theory • Atomic structure • Structure and properties of materials...
- H1 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
Electrochemistry
Structure
How to differentiate:
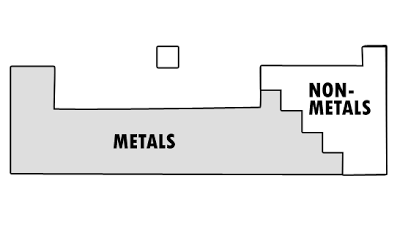
Metal and Non-Metals
- In the Periodic Table, metals are found on the left, non-metals are found on the right.
- Refer to dividing line in Periodic Table.

Covalent and Ionic Compounds
- Basis: Electronegativity difference
| Large | Ionic |
| Small | Covalent |
- The following generalisation is applicable:
| Metal + Non-Metal | Ionic |
| Non-Metal + Non-Metal | Covalent |
Notable Exceptions:
- AlCl3, AlBr3, AlI3
- BeX2
Simple and Giant Molecular Structures
- Memorise the common giant molecules (diamond, graphite, SiO2)
- Can safely regard the rest of the covalent compounds as having simple structures.
- What Is An Activity Series, And How Is It Used?
An activity series is a list of substances ranked in order of relative reactivity. For example, magnesium metal can knock hydrogen ions out of solution, so it is considered more reactive than elemental hydrogen: Mg(s) + 2 H+(aq) H2(g) + Mg2+(aq) Zinc...
- Predict/ Account For Physical Properties
← Back to Chemical Bonding Approach: Determine the type of substance (metal/ ionic/ covalent) and structure (giant metallic/ giant ionic/ giant covalent/ simple molecular) Determine bonding relevant to property Focus on that particular column...
- Chemical Bonding
Overview * Covalent bonds are also present in simple molecular structures. However, they are not broken during physical reactions (e.g. boiling, melting) For questions related to Chemical Bonding: Determine the type of substance (metal/...
- O-level Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
1. Experimental Chemistry • Experimental design • Methods of purification and analysis • Identification of ions and gases 2. The Particulate Nature of Matter • Kinetic particle theory • Atomic structure • Structure and properties of materials...
- H1 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
