Electrochemistry
- Arenes (overview)
← Back to Arenes Structure & Bonding All C atoms in benzene are sp2 hybridised → benzene is planar π e– are delocalised within the benzene ring → (i) added stability due to charge dispersal and (ii) all C–C...
- Alkanes (overview)
Structure & Bonding saturated: all C atoms are bonded to 4 atoms all C atom are sp3 hybridised non-polar simple molecular structures consisting of alkane molecules held together by weak VDW forces ...
- H2 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- H1 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry : 12.5 Organic Reaction
TYPE OF CLEAVAGE : 2 type of bond cleavage:- Hemolytic cleavageHeterolytic cleavage Hemolytic cleavage The breaking of a single (two-electron) bond in which one electron remains on each of the atoms. Also known as free-radical reaction; homolysis. ...
Electrochemistry
Writing Free Radical Substitution Mechanism
← Back to Alkanes
When writing mechanisms:
- It is a good practice to write the name of the mechanism whether or not the question asks for it.
- You just need to show the series of equations/ arrows. There is no need for descriptions i.e. the chlorine molecule undergoes homolytic cleavage to give two chlorine atoms/ radicals.
Common Errors:
- Sloppy naming e.g. ‘substitution’, ‘free radical reaction’ or ‘free substitution’ or ‘FRS’
- Wrong illustration of arrows
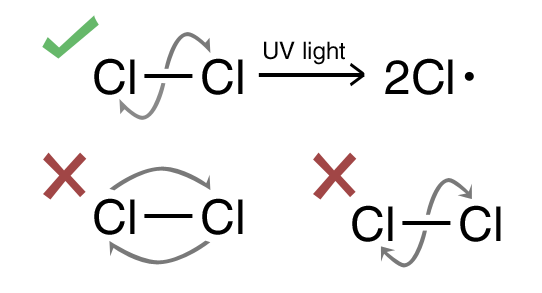
- Forgot to put conditions i.e UV light or heat
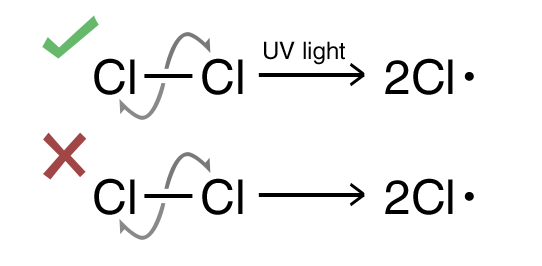
- Use of molecular formula
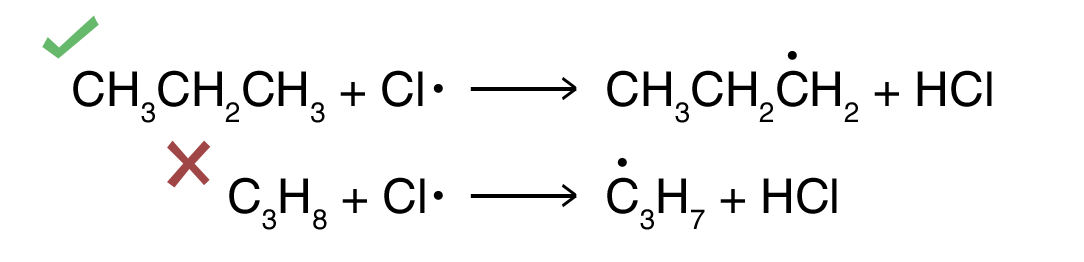
- Wrong halogen.
Under exam conditions, students sometimes use the wrong halogen (i.e. use Cl2 when qns asks for Br2) This happens when they blindly regurgitate what they have memorised.
NOTE:
- C–H bond is relatively strong; it does NOT break during Free Radical Substitution.
- Hence, H · and H2 will never appear in any step of the mechanism.
The second point is often tested in MCQs e.g.
Which of the following species would be present during the free radical chlorination of ethane?
1 · CH2CH3
2 · CH2CH2CH2CH3
3 H2
- Arenes (overview)
← Back to Arenes Structure & Bonding All C atoms in benzene are sp2 hybridised → benzene is planar π e– are delocalised within the benzene ring → (i) added stability due to charge dispersal and (ii) all C–C...
- Alkanes (overview)
Structure & Bonding saturated: all C atoms are bonded to 4 atoms all C atom are sp3 hybridised non-polar simple molecular structures consisting of alkane molecules held together by weak VDW forces ...
- H2 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- H1 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry : 12.5 Organic Reaction
TYPE OF CLEAVAGE : 2 type of bond cleavage:- Hemolytic cleavageHeterolytic cleavage Hemolytic cleavage The breaking of a single (two-electron) bond in which one electron remains on each of the atoms. Also known as free-radical reaction; homolysis. ...
