Electrochemistry
- Substituent Effects
← Back to Arenes A substituent on a benzene ring can have 2 effects: activate or deactivate the ring i.e. cause the substituted benzene to be more reactive or less reactive than benzene direct the position of subsequent substitution i.e. 2,4-directing...
- Determine Products Of Oxidative Cleavage
← Back to Alkenes Cleave the C=C Add O at the end of each dangling C= Check for H bonded to C on C=O (i.e. aldehydes); Add an O to each H directly bonded to C=O (i.e. convert the aldehyde to a carboxylic acid). If the...
- H2 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- H1 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- Electrochemistry : 10.1 Galvanic Cell (continued)
SPONTANEOUS REACTION occurs as the result of different ability of metal to give up their electron to flow through the circuit. CELL POTENTIAL (ECell) different in electrical potential of electrodes also called voltage or electromotive...
Electrochemistry
Assign pH to Amino Acids
← Back to Amino Acids & Proteins
Approach:
- Recall: pKa = – logKa [stronger acid = larger Ka/ smaller pKa]
- R–COOH is a stronger acid than R–NH3+
- –COOH closer to –NH3+ is the stronger acid
- –NH3+ closer to –COOH is the stronger acid.
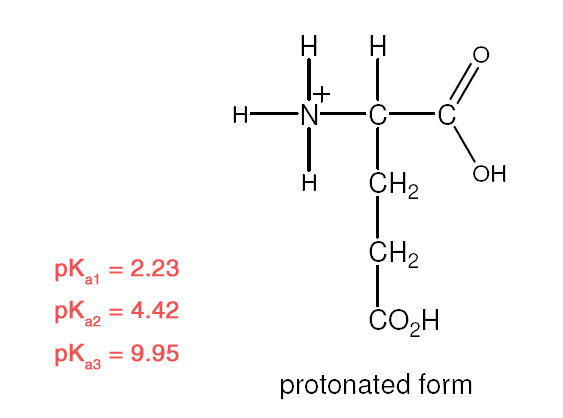
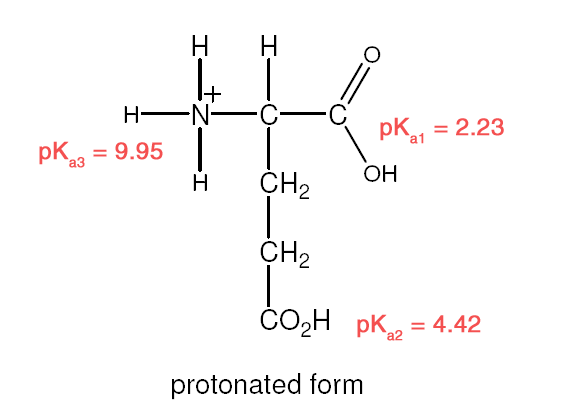
| Example 1 :
Explanation:
|
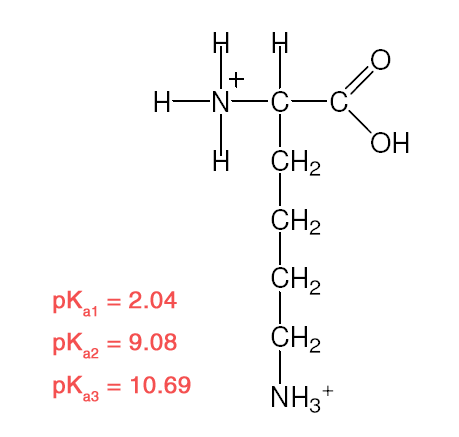
| Example 2 :
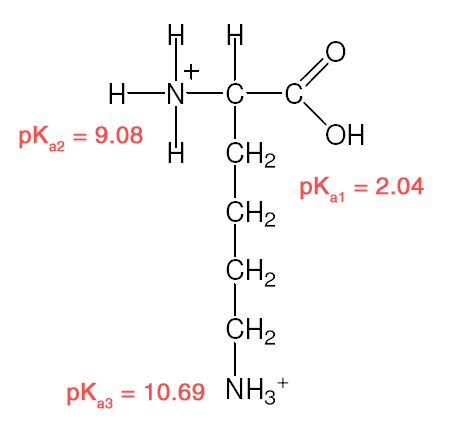 Explanation:
|
- Substituent Effects
← Back to Arenes A substituent on a benzene ring can have 2 effects: activate or deactivate the ring i.e. cause the substituted benzene to be more reactive or less reactive than benzene direct the position of subsequent substitution i.e. 2,4-directing...
- Determine Products Of Oxidative Cleavage
← Back to Alkenes Cleave the C=C Add O at the end of each dangling C= Check for H bonded to C on C=O (i.e. aldehydes); Add an O to each H directly bonded to C=O (i.e. convert the aldehyde to a carboxylic acid). If the...
- H2 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- H1 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
- Electrochemistry : 10.1 Galvanic Cell (continued)
SPONTANEOUS REACTION occurs as the result of different ability of metal to give up their electron to flow through the circuit. CELL POTENTIAL (ECell) different in electrical potential of electrodes also called voltage or electromotive...