Electrochemistry
- Substituent Effects
← Back to Arenes A substituent on a benzene ring can have 2 effects: activate or deactivate the ring i.e. cause the substituted benzene to be more reactive or less reactive than benzene direct the position of subsequent substitution i.e. 2,4-directing...
- Alkenes (notes)
← Back to Alkenes Hydrogenation Type of Reaction: Reduction/ Addition Hydrogenation is NOT an electrophilic addition reaction; the mechanism is solid state catalysed (adsorption) and does not involve an electrophile. Alkenes do not react...
- Alkenes
NOTES: Overview Notes TYPES OF QUESTIONS: Determine Products of Electrophilic Addition Reactions Determine Products of Oxidative Cleavage ...
- Assign Ph To Amino Acids
← Back to Amino Acids & Proteins Approach: Recall: pKa = – logKa [stronger acid = larger Ka/ smaller pKa] R–COOH is a stronger acid than R–NH3+ –COOH closer to –NH3+ is the stronger acid –NH3+ closer to –COOH is the stronger...
- Reactions
← Back to Organic Chemistry Problem-Solving Approach There are 4 types of questions: Given reactants + products → suggest reagents and conditions Given reactants + reagents → suggest products Given new reaction (Grignard, Killiani-Fishcer,...
Electrochemistry
Determine Products of Oxidative Cleavage
← Back to Alkenes
|
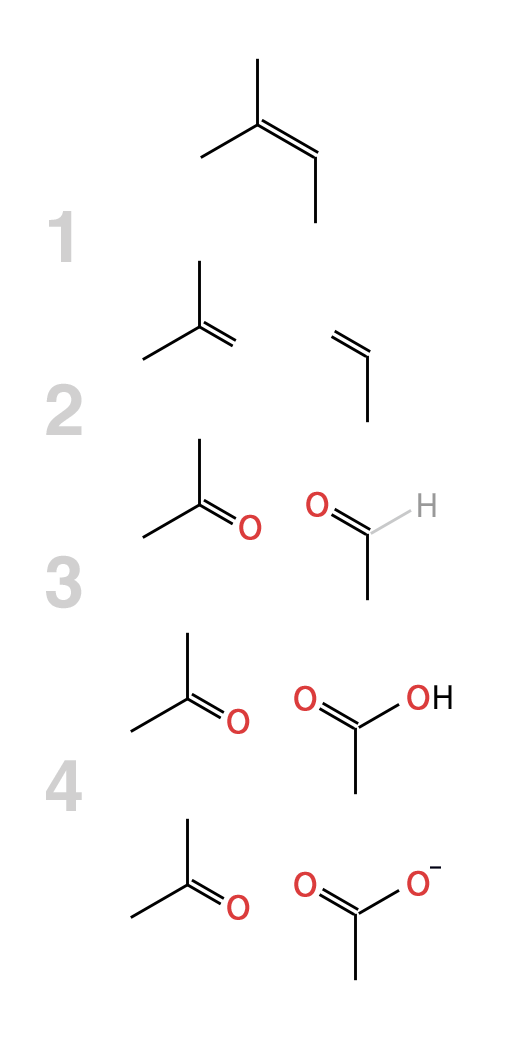
Example: Determine the products when 2-methyl-but-2-ene, (CH3)2C=CHCH3 is reacted with hot alkaline KMnO4.

- Substituent Effects
← Back to Arenes A substituent on a benzene ring can have 2 effects: activate or deactivate the ring i.e. cause the substituted benzene to be more reactive or less reactive than benzene direct the position of subsequent substitution i.e. 2,4-directing...
- Alkenes (notes)
← Back to Alkenes Hydrogenation Type of Reaction: Reduction/ Addition Hydrogenation is NOT an electrophilic addition reaction; the mechanism is solid state catalysed (adsorption) and does not involve an electrophile. Alkenes do not react...
- Alkenes
NOTES: Overview Notes TYPES OF QUESTIONS: Determine Products of Electrophilic Addition Reactions Determine Products of Oxidative Cleavage ...
- Assign Ph To Amino Acids
← Back to Amino Acids & Proteins Approach: Recall: pKa = – logKa [stronger acid = larger Ka/ smaller pKa] R–COOH is a stronger acid than R–NH3+ –COOH closer to –NH3+ is the stronger acid –NH3+ closer to –COOH is the stronger...
- Reactions
← Back to Organic Chemistry Problem-Solving Approach There are 4 types of questions: Given reactants + products → suggest reagents and conditions Given reactants + reagents → suggest products Given new reaction (Grignard, Killiani-Fishcer,...
