Determine Structure of Undigested Protein
← Back to Amino Acids & Proteins
Digestion of proteins can be carried out using 2 methods:
| Acid-Base Hydrolysis | Enzyme Cleavage |
|
|
Approach
| Acid-Base Hydrolysis | Enzyme Cleavage |
|
|
| Example (Hydrolysis):
Partial hydrolysis of a polypeptide produced the following fragments:
asp – lys – gly val – phe – asp lys – val – phe gly – phe – lys
Determine the structure of the undigested polypeptide.
Spot repetition of residues in fragments 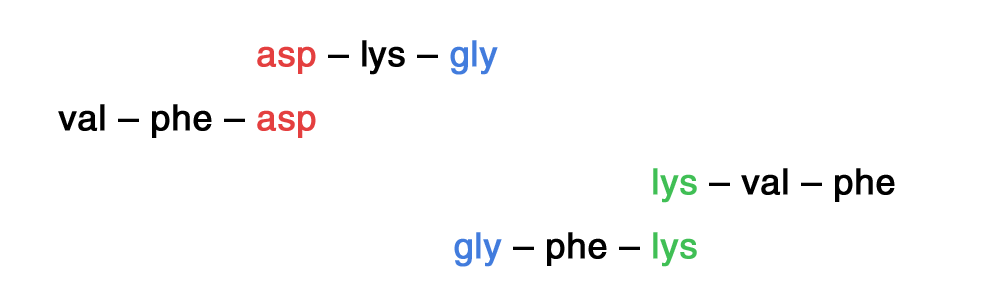
Structure: val – phe – asp – lys – gly – phe – lys – val – phe |
| Example (Enzyme):
A polypeptide was digested with 2 different enzymes. For each enzyme, the following fragments were obtained.
Determine the structure of the undigested polypeptide.
Step 1: Determine terminal residues; common in 2 sets of data 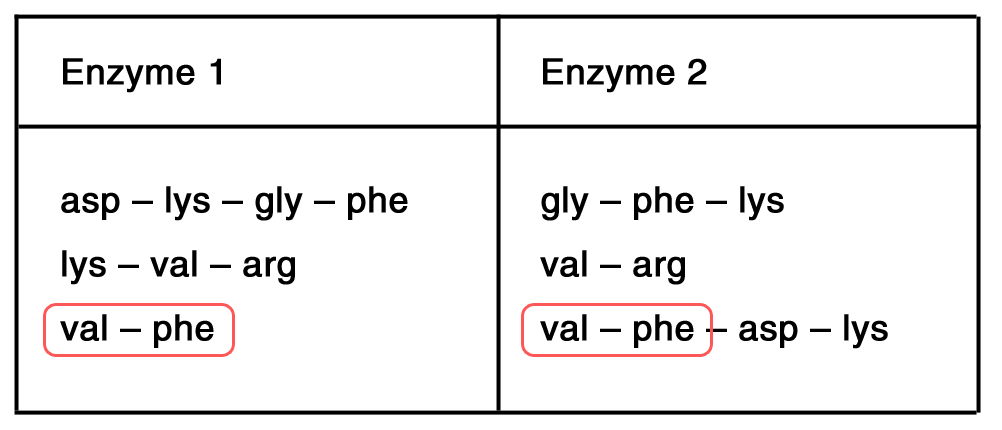 → left terminal: val – phe
Step 2: Spot repetition between the sets of data 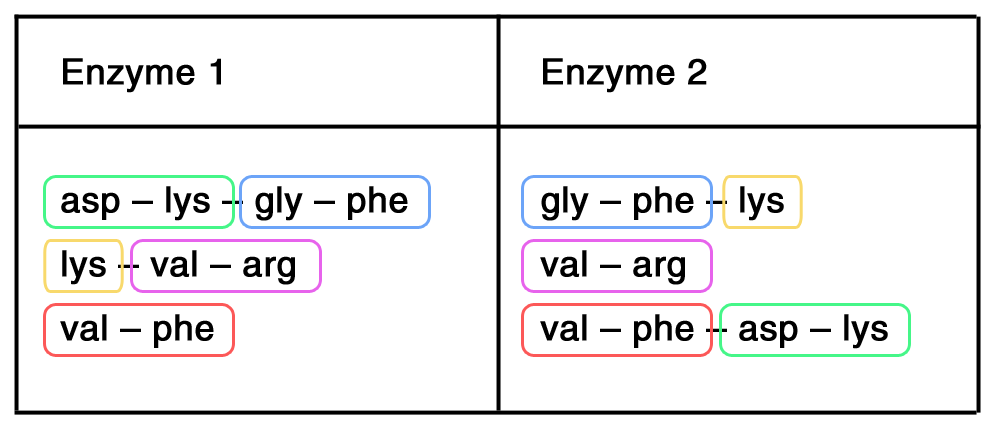 Green: From Enzyme 2, we can determine: val – phe is followed asp – lys
Blue: From Enzyme 1, we can determine: val – phe – asp – lys is followed by gly – phe
Yellow: From Enzyme 2, we can determine: val – phe – asp – lys – gly – phe is followed by lys
Purple: From Enzyme 1, we can determine: val – phe – asp – lys – gly – phe – lys is followed by val – phe
Structure: val – phe – asp – lys – gly – phe – lys – val – phe |
- Chemical Bonding
NOTES: TYPES OF QUESTIONS: Determine Structure and Bonding Draw Dot-Cross Diagrams Determine Type of Bonding for Simple Molecules Predict/ Account for Physical Properties ...
- Determine Structure & Bonding
← Back to Chemical Bonding Determine Structure: Structure Metals Giant Ionic Lattice Ionic Compounds Giant Ionic Lattice Covalent Compounds Giant/ Simple Molecule Structure Metal and Non-Metals...
- Distinguishing
← Back to Organic Chemistry Problem-Solving Approach Approach: Spot the difference: FG or structure? FG: Use a test specific to the FG present in only one of the two compounds. Structure: Most of the time → Iodoform or selective oxidation...
- Ionic Equilibria (acid/ Base)
There are two broad aspects of this chapter: Acid/ Base Equilibria Solubility Equilibria Acid/ Base Equilibria Important Relations p = -log10 At 25°C: pH + pOH = pKw = 14 pKa + pKb = 14 [H+][OH–] = 10-14 Ka x Kb = Kw = 10-14 Approach:...
- H2 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
