Standard Electrode Potential (SEP)
← Back to Electrochemistry
How to draw the set-up for measuring SEP?
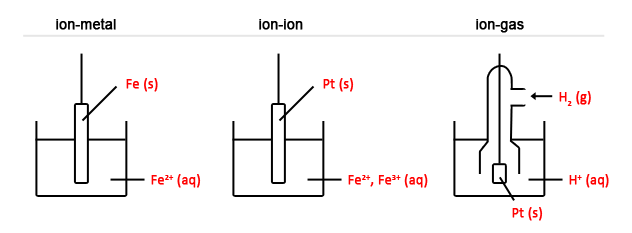
- Learn to draw the 3 types of half cells: (1) ion-metal (2) ion-ion (3) ion-gas.
- Determine the type of half cell the qns is asking for.
- Connect the half cell to SHE.
3 types of half cells:
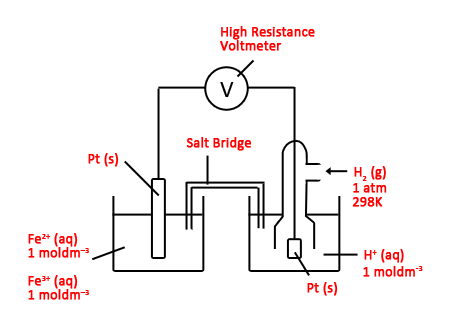
| Example: Draw the setup for measuring E⁰Fe3+/Fe2+
Fe3+/Fe2+ is an ion-ion half cell H+/H2 (SHE) is an ion-gas half cell
Note: 1. Ensure all parts are labeled e.g. salt bridge. 2. Ensure standard conditions for all reagents i.e. - 1 atm, 298 K for gases - 1 mol dm–3 for solutions |
How to draw a cell diagram?
Cell diagram is a simplified representation of a galvanic cell.
- Anode on the left; Cathode on the right; Salt bridge (represented as ||) in the middle i.e. Anode || Cathode
- Electrodes at extreme ends.
- Anode half cell (oxidation) write species in increasing oxidation no.; Cathode half cell (reduction) write species in decreasing oxidation no.
- Use ‘,’ to separate species in the same phase; Use ‘|’ to separate species in different phases.
| Example: Draw the cell diagram for the cell represented above.
1. Since E⁰Fe3+/Fe2+ = +0.77 V (more + than SHE), it must be the cathode. (anode) SHE || Fe3+/Fe2+ (cathode)
2. Electrodes at extreme ends Pt SHE || Fe3+/Fe2+ Pt
3. Anode (increasing ON); Cathode (decreasing ON) Pt H2 H+ || Fe3+ Fe2+ Pt
4. Same phase (,); Different phase (|) Pt (s) | H2 (g) | H+ (aq) || Fe3+ (aq) , Fe2+ (aq) | Pt (s) |
- Reference Electrodes
In most electrochemical experiments our interest is concentrated on only one of the electrode reactions. Since all measurements must be on a complete cell involving two electrode systems, it is common practice to employ a reference...
- Cell Description Conventions
In order to make it easier to describe a given electrochemical cell, a special symbolic notation has been adopted. In this notation the cell we described above would be Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s) There are several other conventions relating...
- Electrochemistry : 10.3 : Electrolysis Cell
VOLTAN CELL VS ELECTRIOLYSIS CELL . Voltaic cell :use a spontaneous reaction to generate electric energy. Electrolysis :use electric energy to drive non- spontaneous energy. VOLTAIC CELL. ELECTROLYTICelectrons generate...
- Electrochemistry : 10.1 Galvanic Cell (continued)
SPONTANEOUS REACTION occurs as the result of different ability of metal to give up their electron to flow through the circuit. CELL POTENTIAL (ECell) different in electrical potential of electrodes also called voltage or electromotive...
- Electrochemistry : 10.1 Galvanic Cell
Electrochemistry Study of relationship between chemical change & electric work Oxidation Loss of electron by species accompanied byn an increase in oxidation number Ex: Reduction Gain electron by a species accompanied by a decrease number...