Electrochemistry
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELL
There are two type :
VOLTAIC CELL
ELECTROLYTIC CELL
ELECTRODES
INACTIVE ELECTRODE
ANODE & CATHODE
ELECTROLYTE
ESSENTIAL IDEA OF VOLTAIC CELL
OXIDATION HALF CELL
REDUCTION HALF CELL
RELATIVE CHARGE ON ELECTRODES
SALT BRIDGE
- Reference Electrodes
In most electrochemical experiments our interest is concentrated on only one of the electrode reactions. Since all measurements must be on a complete cell involving two electrode systems, it is common practice to employ a reference...
- Galvanic Cells
This arrangement is called a Galvanic cell. A typical cell might consist of two pieces of metal, one zinc and the other copper, each immersed each in a solution containing a dissolved salt of the corresponding metal. The two...
- Standard Electrode Potential (sep)
← Back to Electrochemistry How to draw the set-up for measuring SEP? Learn to draw the 3 types of half cells: (1) ion-metal (2) ion-ion (3) ion-gas. Determine the type of half cell the qns is asking for. Connect the half cell to SHE. ...
- How To Balance Ionic Equations In Alkaline Medium?
(I) Standard Electrode Potential What information can we obtain from SEP? Sign – oxidation or reduction favoured Magnitude – the extent the reaction is favoured How to measure SEP? - connecting the redox couple (half cell) to SHE. - learn to draw...
- Electrochemistry : 10.3 : Electrolysis Cell
VOLTAN CELL VS ELECTRIOLYSIS CELL . Voltaic cell :use a spontaneous reaction to generate electric energy. Electrolysis :use electric energy to drive non- spontaneous energy. VOLTAIC CELL. ELECTROLYTICelectrons generate...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry : 10.1 Galvanic Cell
Electrochemistry
- Study of relationship between chemical change & electric workOxidation
- Loss of electron by species accompanied byn an increase in oxidation number
Ex: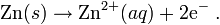
Reduction - Gain electron by a species accompanied by a decrease number of oxidationEx:

Redox reaction - Process which there are net movement of electrons from one reactant to another
- Also called oxidation – reduction process.
- Oxidation and reduction occur at the same time.Ex:
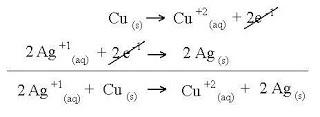 Oxidizing agent
Oxidizing agent- Substance that accepts electron in redox reaction and undergoes decrease number of oxidation.
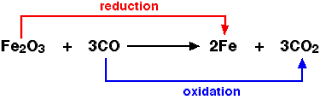 O.A is Fe2O3Reducing agent
O.A is Fe2O3Reducing agent - Substance that donate electron in redox reaction and undergoes an increase oxidation number.Ex:
 CO is an reducing agentThree key point
CO is an reducing agentThree key point - Oxidation always accompany by reduction
- Oxidizing agent reduced reducing agent oxidised
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELL
There are two type :
- Voltaic cell
- Electrolytic cell
VOLTAIC CELL
- Use spontaneous reaction to generate electric energy
- System does work on surrounding
- All batteries contains voltaic cell
ELECTROLYTIC CELL
- Use electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous reaction
- Surrounding do work on system
- Ex: electroplating & recovering metal from ores
ELECTRODES
- Object that conduct electricity between cell and surrounding
- 2 electrode (anode & cathode) are dipped into electrolyte
- ACTIVE ELECTRODES
- Involve in half reaction
- Ex: zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), Iron (Fe)
INACTIVE ELECTRODE
- If no reactant or product can be uses as electrode
- Ex: graphite (C), Platinum (Pt)
- The electrolyte solution contain all species involved in the half – reaction
ANODE & CATHODE
- Oxidation half reaction takes place at cathode
- Electron given up by substance being oxidised (reducing agent) and leave the cell at anode
- Reducing half reaction takes place at cathode
- Electron are taken up by substance being reduced (oxidizing agent) & enters the cell at cathode
ELECTROLYTE
- Mixture of ions (usually in aqueos solution) that are involved in reaction or that carry charge.
ESSENTIAL IDEA OF VOLTAIC CELL
- Component of each half reaction (half – cell) are placed in a seperate container
- The two half cell are joined by circuit which consist a wire and a salt bridge
OXIDATION HALF CELL
- Metal bar (anode) is immersd in Zn2+ electrolyteEx: ZnSO4
- Zn is reactant in oxidation half reaction
- Zn conduct electricity and release electron out of its half cell
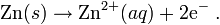
- Mass of Zn electrode decrease
REDUCTION HALF CELL
- A Cu metal bar (cathode) is immersed in a Zn2+ electrolyte
- Ex: CuSO4 solution
- Cu is a product in reduction half reaction
- Cu conducts electricity and released electron into itself.

- Mass of copper electrode increase
RELATIVE CHARGE ON ELECTRODES
- Anode:
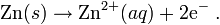
- Electron flow from anode to cathode through wire
- Cathode

- Electron are continously generated at anode * consume at cathode
SALT BRIDGE
- Contains a solution of non-reacting ion such as KCl,KNO3, Na2SO4 acts as liquid wire (allowing ions to flow & complete the circuit.
HOW DOES THE CELL MAINTAIN ITS ELECTRICAL NEUTRALITY
| Anode Half Cell | Cathode Half Cell |
| Zn 2+ ions enters the solution causing the excess of positive charge. | Cu2+ ions leave the solution causing the excess of negative charge |
| Cl- ions from the salt bridge move into anode (Zn) half cell | K+ ions from salt bridge move into cathode Cu half cell |
CELL NOTATION
- Ex : Zn(s) l Zn2+ (aq) l l Cu2+ (aq) l Cu(s)
- Anode left, cathode right
- 'l' represent phase boundary
- Use ',' for component that are in the same phaseGraphite l I- (aq) l I(s) l l H+ (aq), MnO4- (aq), Mn2+ (aq) l graphite
- Sometimes we specify the concentration of dissolved componentZn(s) l Zn2+ (1 M) l Cu2+ (1 M) l Cu(s)
- Electrode appear ait far right and left notation.
- Half-cell component usually appear in the same order as in the half-reaction
Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e- ------ Cu (s) (reducing)
Zn(s) ------ Zn2+ (aq) + 2e- (oxidizing)
Cu 2+ (aq) + Zn(s) ------ Cu (s) + Zn2+ (aq) (overall)
- Reference Electrodes
In most electrochemical experiments our interest is concentrated on only one of the electrode reactions. Since all measurements must be on a complete cell involving two electrode systems, it is common practice to employ a reference...
- Galvanic Cells
This arrangement is called a Galvanic cell. A typical cell might consist of two pieces of metal, one zinc and the other copper, each immersed each in a solution containing a dissolved salt of the corresponding metal. The two...
- Standard Electrode Potential (sep)
← Back to Electrochemistry How to draw the set-up for measuring SEP? Learn to draw the 3 types of half cells: (1) ion-metal (2) ion-ion (3) ion-gas. Determine the type of half cell the qns is asking for. Connect the half cell to SHE. ...
- How To Balance Ionic Equations In Alkaline Medium?
(I) Standard Electrode Potential What information can we obtain from SEP? Sign – oxidation or reduction favoured Magnitude – the extent the reaction is favoured How to measure SEP? - connecting the redox couple (half cell) to SHE. - learn to draw...
- Electrochemistry : 10.3 : Electrolysis Cell
VOLTAN CELL VS ELECTRIOLYSIS CELL . Voltaic cell :use a spontaneous reaction to generate electric energy. Electrolysis :use electric energy to drive non- spontaneous energy. VOLTAIC CELL. ELECTROLYTICelectrons generate...
