Electrochemistry
- Alkenes (overview)
← Back to Alkenes Structure & Bonding unsaturated: contain C=C C atoms in C=C are sp2 hybridised non-polar simple molecular structures consisting of alkene molecules held together by weak VDW forces ...
- Alkenes
NOTES: Overview Notes TYPES OF QUESTIONS: Determine Products of Electrophilic Addition Reactions Determine Products of Oxidative Cleavage ...
- Titration
← Back to AMS Normal Titration See general approach for chemical calculations. Example: 25.00 cm3 of 0.100 moldm–3 Na2CO3 solution was titrated against 0.200 moldm–3 HCl. Determine the volume of HCl required...
- How To Draw Dot-cross Diagram
← Back to Chemical Bonding 1 Determine the central atom and surrounding atoms. Central atom is commonly the: - Element with the lesser no. of atoms - First element in chemical formula (except H) - Least electronegative...
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry : 12.5 Organic Reaction
TYPE OF CLEAVAGE : 2 type of bond cleavage:- Hemolytic cleavageHeterolytic cleavage Hemolytic cleavage The breaking of a single (two-electron) bond in which one electron remains on each of the atoms. Also known as free-radical reaction; homolysis. ...
Electrochemistry
Determine Products of Electrophilic Addition Reactions
← Back to Alkenes
|
Question. When alkenes are reacted with mixed halogens e.g. I―Cl, which atom is the electrophile; which atom is added to the C=C first?
Answer. Compare the electronegativity of the halogens. The less electronegative element is the electrophile; it is added first and to the C with more H.
Example (for 1+2):
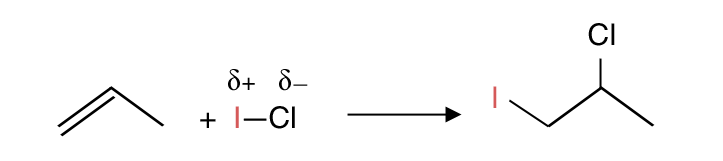
- I is less electronegative compared to Cl
- I is added first and to the C with more H
Example (for 3):
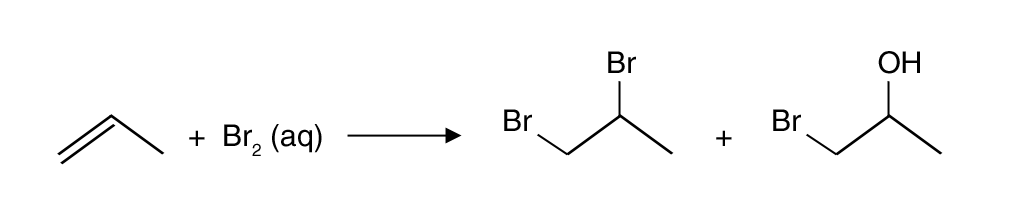
- Reagent used is Br2 (aq) [c.f. Br2 (in CCl4)]
- There are two possible nucleophiles in the 2nd step: Br– and H2O
- A mixture of products would be obtained
- Alkenes (overview)
← Back to Alkenes Structure & Bonding unsaturated: contain C=C C atoms in C=C are sp2 hybridised non-polar simple molecular structures consisting of alkene molecules held together by weak VDW forces ...
- Alkenes
NOTES: Overview Notes TYPES OF QUESTIONS: Determine Products of Electrophilic Addition Reactions Determine Products of Oxidative Cleavage ...
- Titration
← Back to AMS Normal Titration See general approach for chemical calculations. Example: 25.00 cm3 of 0.100 moldm–3 Na2CO3 solution was titrated against 0.200 moldm–3 HCl. Determine the volume of HCl required...
- How To Draw Dot-cross Diagram
← Back to Chemical Bonding 1 Determine the central atom and surrounding atoms. Central atom is commonly the: - Element with the lesser no. of atoms - First element in chemical formula (except H) - Least electronegative...
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry : 12.5 Organic Reaction
TYPE OF CLEAVAGE : 2 type of bond cleavage:- Hemolytic cleavageHeterolytic cleavage Hemolytic cleavage The breaking of a single (two-electron) bond in which one electron remains on each of the atoms. Also known as free-radical reaction; homolysis. ...
