Dilution versus Sampling
← Back to AMS
Analogy
Imagine the scenario where a sachet of milo powder is dissolved in 100 cm3 of water.
Dilution – Another 100 cm3 of water is added to the solution.
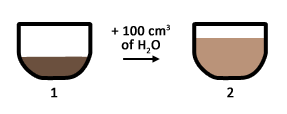
- Is the amount of milo powder the same in 1 & 2?
- Is the sweetness of 1 & 2 the same?
Sampling – 100 cm3 of the milo solution is poured into a second cup.
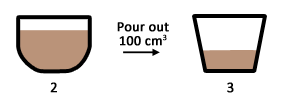
- Is the amount of milo powder the same in 2 & 3?
- Is the sweetness of 2 & 3 the same?
From the above analogy, you should be able to distinguish between the consequences of dilution & sampling.
| Dilution | Sampling |
| No. of moles unchanged | No. of moles changed ns = c x Vs ns: amount of substance in sample (mol) Vs: vol. of sample |
| Conc. changed ci Vi = cf Vf ci Vi: conc. & vol. before dilution cf Vf:conc. & vol. after dilution | Conc. unchanged |
It is important to highlight the presence of ‘dilution’ and/ or ‘sampling’ in a question. Often, students fail to account for them which results in incomplete answers.
| Example 10 cm3 of HCl was diluted to 250 cm3 with deionised water. A 25 cm3 aliquot of the diluted solution required 16.00 cm3 of 0.05 moldm–3 NaOH for complete neutralisation. Calculate the concentration of the undiluted HCl.
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
nNaOH = 16/1000 x 0.05 = 8.0 x 10–4 mol nHCl in 25 cm3 = nNaOH = 8.0 x 10–4 mol nHCl in 250 cm3 = 8.0 x 10–3 mol cHCl = 8.0 x 10–3 / (10/1000) = 0.8 moldm–3
Common Error #1 (Neglect sampling) nNaOH = 16/1000 x 0.05 = 8.0 x 10–4 mol nHCl = nNaOH = 8.0 x 10–4 mol cHCl = 8.0 x 10–4 / (10/1000) = 0.08 moldm–3 Common Error #2 (Neglect dilution) cHCl VHCl = cNaOH VNaOH cHCl x 25/1000 = 0.05 x 16/1000 cHCl = 0.032 moldm–3 |
- Tfdo Synthesis Procedure
TFDO aka methyl(trifluoromethyl)dioxirane is a very powerful reagent for the C–H oxidation of unactivated alkanes. Unfortunately, it is not commercially available and consequently needs to be prepared. Due to the volatility of TFDO, its preparation...
- Ppm/ Ppb
← Back to AMS Parts per million, ppm is just another unit of concentration (like mol dm–3, g dm–3 etc) i.e. 1 part solute in 1 million parts solvent. For solutions, it simply means the grams of solute per million grams of solution....
- 6 Tips To Ace Your 'a' Level Chemistry
Tip #01 - Understand AND memorise key definitions, equations and concepts. Tip #01 is of fundamental importance. Working on the other tips without fulfilling Tip #01 will gain you limited results. But I got an A for my 'O' levels...
- Ionic Equilibria (acid/ Base)
There are two broad aspects of this chapter: Acid/ Base Equilibria Solubility Equilibria Acid/ Base Equilibria Important Relations p = -log10 At 25°C: pH + pOH = pKw = 14 pKa + pKb = 14 [H+][OH–] = 10-14 Ka x Kb = Kw = 10-14 Approach:...
- Titration
← Back to AMS Normal Titration See general approach for chemical calculations. Example: 25.00 cm3 of 0.100 moldm–3 Na2CO3 solution was titrated against 0.200 moldm–3 HCl. Determine the volume of HCl required...
