Electrochemistry
- Making C–c Bonds With The Simplicity Of Making Amide Bonds
Despite all of the wonderful advances in organic synthesis, amide-bond formation is still the most widely used reaction among those making medicines. This truth has led some to declare their embarrassment and depression. Medicinal...
- Hey! We Used C-h Activation To Make A Natural Product!
Once upon a time, we were interested making fumitremorgin A... Phil's interest in verruculogen and fumitremorgin A has been long standing (see: Austamine and Okaramine), but strangely the endoperoxide-containing indole alkaloids haven't...
- A Tale Of Two Olefins
A prototype of the graphical abstract that Phil didn't want to submit to JACS.Today marks the day that another paper makes its way out of the hot little presses of the ACS Publication Office and into the world of chemistry. This time, it's a...
- Reflecting On Yield, And The Need For A Qualitative Assessment Of Reactions
Here's some thoughts: 1. I categorize all reaction yields qualitatively. What does this mean? Generally speaking, I don't really believe in yields other than 0%, 25%, 50%, 75%, or quantitative. I also sometimes break this down as 1.)...
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry : 12.5 Organic Reaction
TYPE OF CLEAVAGE : 2 type of bond cleavage:- Hemolytic cleavageHeterolytic cleavage Hemolytic cleavage The breaking of a single (two-electron) bond in which one electron remains on each of the atoms. Also known as free-radical reaction; homolysis. ...
Electrochemistry
Tales from the Trenches: Pallambins
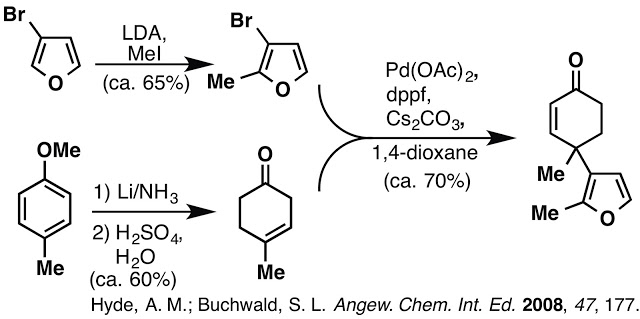
Our total synthesis of Pallambins C and D is out today in JACS. We have placed a summary of our failed approaches and strategies in the supporting information to give the reader a glimpse of what went into developing our synthetic route. Here we highlight a few reactions and problems encountered during this work. Our early approach began with the gamma-arylation of a beta,gamma-unsaturated ketone. We found these conditions worked well, but as the synthesis progressed and more material was required to keep the synthesis moving forward we noted severely decreased yields as the scale of the reaction increased. Careful observation of the reaction mixture itself revealed that the catalyst, ligand and base created a heterogeneous solution which clumped up and accumulated at the liquid/gas interface of the round bottom flask. This clumping limited the reaction to 2 mmol scale before seeing a steep drop in yield from ca. 70% to ca. 20%. We resorted to setting up many 2 mmol scale reactions in parallel, but this was a cumbersome and not very efficient work around the issue.
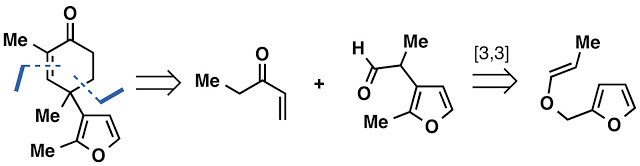
A Morton flask may have been a solution to this problem, but we did not have one available in lab and purchasing one would not solve all the issues with this approach. The cost of 3-bromofuran was high (to begin a synthesis from), the stoichiometric use of Cs2CO3 was necessary (we examined various bases) but not ideal and the enone delivered from this method lacked an alpha-methyl group. The sum of these issues led us to examine an alternative Robinson annulation disconnection of the enone revealing ethyl vinyl ketone and a furanoaldehyde. This aldehyde could arise from a Claisen rearrangement of the corresponding allyl vinyl ether.
Although the aldehyde was known in the literature, we found the reported 20% yield of the product to be an unbreakable barrier for the classic Claisen rearrangement despite our best attempts at catalysis and variation of reaction conditions. Ultimately the Eschenmoser-Claisen rearrangement emerged as the superior reaction, but instead delivered an amide rather than the desired aldehyde necessitating a reduction. Surprisingly, DIBAL reduction of the amide was sluggish and only reached 50% conversation. This was both frustrating and frightening as we did not have a way to adequately supply material to the front line of the synthesis. Fortunately, an examination of various reported methods led us to the use of tetramethyldisiloxane (TMDS) in the presence of Ti(OiPr)4 to achieve the desired reduction of the amide to an aldehyde in the same pot as the Eschemoser-Claisen rearrangement in 75% overall yield.
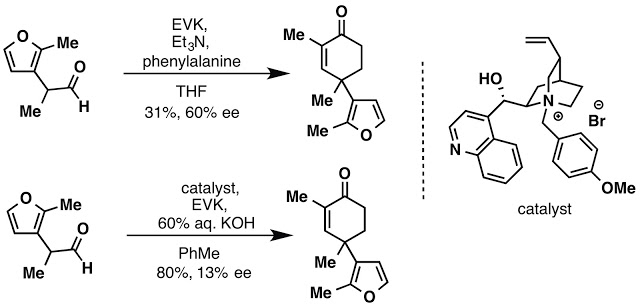
Why isn’t the Robinson annulation asymmetric?
We examined various options in pursuit of an asymmetric synthesis with little success. Although we were able to achieve some degree of asymmetric induction using phenylalanine, the yield of the reaction remained low despite optimization efforts. The use of asymmetric phase transfer conditions increased the yield of the desired enone, but we observed a large drop in ee.
Although phase transfer conditions did not deliver the level of ee we desired, the increased yield was welcomed as the previous conditions for the Robinson annulation used LiOH in isopropanol to deliver the enone in ca. 50%. We briefly revisited Buchwald’s gamma-arylation conditions in our quest for ee. Sadly, after a small ligand screen it became apparent that this would be a lengthy and rather expensive endeavor leading to the abandonment of an asymmetric synthesis all together. Steps 3-11 are discussed to some degree in either the text or supporting information and we are more than happy to answer any question you may have regarding these steps in the comments.
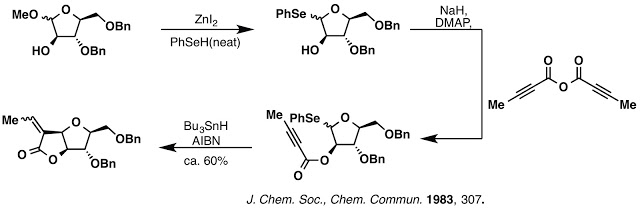
Selenophenol (things I had to work with)
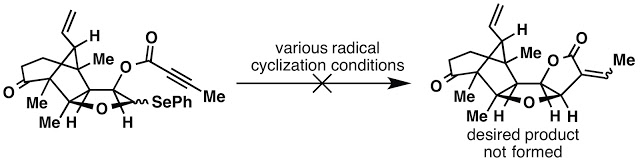
As many of you know Derek Lowe’s In The Pipeline blog sometimes features “Things I Won’t Work With”. One particular entry describes selenophenol (PhSeH) in all of its stinky glory. After the failure of several endgame strategies we considered a radical cyclization approach to D-ring formation. Attempts to install various radical precursors at the anomeric position were surprisingly unsuccessful except for one, PhSeH. Completion of the synthesis seemed so close at the time that we decided to go ahead and use PhSeH. Unfortunately, installation of the selenoacetal required the use of PhSeH as a solvent in the presence of ZnI2. We attempted to use PhSeH in quantities up to a 1:1 solvent mixture with MeCN with no success, leaving no option other than using PhSeH as the solvent. The selenoacetal was installed on a model substrate (the Claisen rearrangement yield problem had not been solved at this point) followed by installation of an alkynoate. Treatment of the alkynoate model substrate with Bu3SnH and AIBN resulted in formation of the desired [3.3.0]furanofuranone system on the model substrate in good yield.
To our dismay, the success of this radical cyclization on the model substrate did not translate to the pallambin system. We explored various methods for radical generation, reaction concentration, rate of addition and everything else we could try to reproduce the result of the model substrate over the course of 2 months with no positive result. This was very tough and stinky time in lab.
Generation of PhSeH from PhSeSePh and the subsequent distillation was a nightmare! The smell of PhSeH is something along the lines of a dumpster filled with rotting skunks set on fire. One afternoon while working with PhSeH a drop of the disgusting liquid fell on one of my gloves unnoticed. I briefly removed my hand from the fume hood and passed it near my face while reaching for something and my head was instantly knocked back by the apocalyptic smell of PhSeH. This small but concentrated exposure resulted in the complete loss of my sense of smell for about 10 days. This was the absolute final straw for PhSeH and the approach was abandoned altogether. It was quite terrifying once I passed the 7 day mark with no sense of smell. I felt like I had made an irreversible mistake that would effect the rest of my life. Fortunately, my sense of smell returned over the course of 3 weeks, but even a year later I’m still haunted by phantom PhSeH smells.
-Luisruben P. Martinez
- Making C–c Bonds With The Simplicity Of Making Amide Bonds
Despite all of the wonderful advances in organic synthesis, amide-bond formation is still the most widely used reaction among those making medicines. This truth has led some to declare their embarrassment and depression. Medicinal...
- Hey! We Used C-h Activation To Make A Natural Product!
Once upon a time, we were interested making fumitremorgin A... Phil's interest in verruculogen and fumitremorgin A has been long standing (see: Austamine and Okaramine), but strangely the endoperoxide-containing indole alkaloids haven't...
- A Tale Of Two Olefins
A prototype of the graphical abstract that Phil didn't want to submit to JACS.Today marks the day that another paper makes its way out of the hot little presses of the ACS Publication Office and into the world of chemistry. This time, it's a...
- Reflecting On Yield, And The Need For A Qualitative Assessment Of Reactions
Here's some thoughts: 1. I categorize all reaction yields qualitatively. What does this mean? Generally speaking, I don't really believe in yields other than 0%, 25%, 50%, 75%, or quantitative. I also sometimes break this down as 1.)...
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry : 12.5 Organic Reaction
TYPE OF CLEAVAGE : 2 type of bond cleavage:- Hemolytic cleavageHeterolytic cleavage Hemolytic cleavage The breaking of a single (two-electron) bond in which one electron remains on each of the atoms. Also known as free-radical reaction; homolysis. ...
