Electrochemistry
- Substituent Effects
← Back to Arenes A substituent on a benzene ring can have 2 effects: activate or deactivate the ring i.e. cause the substituted benzene to be more reactive or less reactive than benzene direct the position of subsequent substitution i.e. 2,4-directing...
- Arenes (overview)
← Back to Arenes Structure & Bonding All C atoms in benzene are sp2 hybridised → benzene is planar π e– are delocalised within the benzene ring → (i) added stability due to charge dispersal and (ii) all C–C...
- Determine Products Of Oxidative Cleavage
← Back to Alkenes Cleave the C=C Add O at the end of each dangling C= Check for H bonded to C on C=O (i.e. aldehydes); Add an O to each H directly bonded to C=O (i.e. convert the aldehyde to a carboxylic acid). If the...
- Determine No. Of Structural Isomers
← Back to Intro to Org Chem [Bad News] There is no mathematical formula available to calculate the number of structural isomers. You have to draw out all possible structures. [Good News] There is a general approach for that. ...
- H1 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
Electrochemistry
Determine Products of Side Chain Oxidation
← Back to Arenes
|
Example:
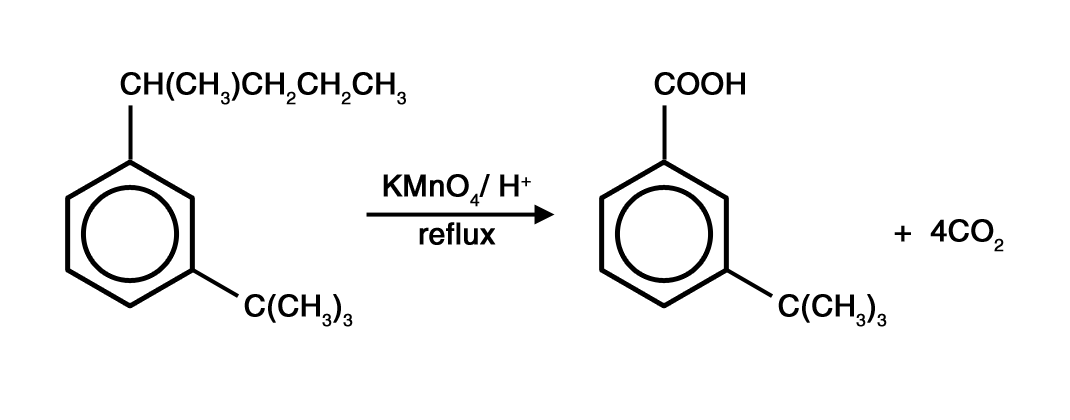
Question. What happens when there exist C=C in the side chain.
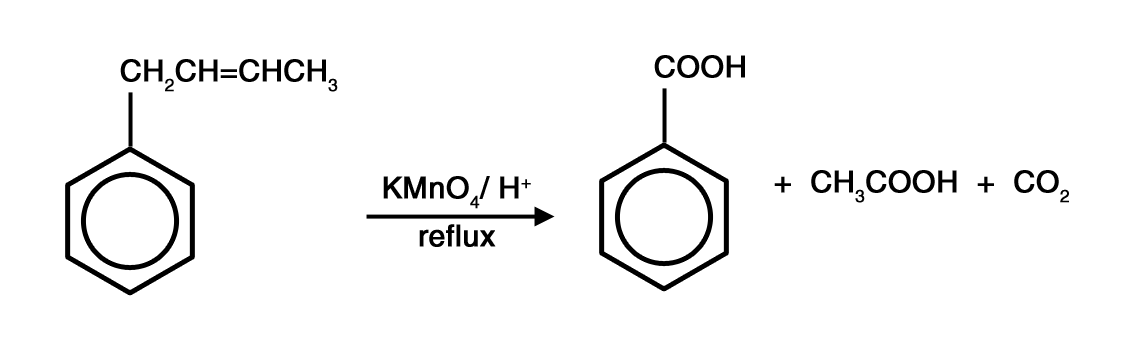
Answer. It is relatively easier to oxidise a C=C than the benzene side chain. Hence, you have to first perform an oxidative cleavage of the C=C and write down the oxidized product of the fragment not attached to the benzene ring.
Then perform a side chain oxidation to oxidise the remaining fragment to give benzoic acid and CO2.
Example:
- Substituent Effects
← Back to Arenes A substituent on a benzene ring can have 2 effects: activate or deactivate the ring i.e. cause the substituted benzene to be more reactive or less reactive than benzene direct the position of subsequent substitution i.e. 2,4-directing...
- Arenes (overview)
← Back to Arenes Structure & Bonding All C atoms in benzene are sp2 hybridised → benzene is planar π e– are delocalised within the benzene ring → (i) added stability due to charge dispersal and (ii) all C–C...
- Determine Products Of Oxidative Cleavage
← Back to Alkenes Cleave the C=C Add O at the end of each dangling C= Check for H bonded to C on C=O (i.e. aldehydes); Add an O to each H directly bonded to C=O (i.e. convert the aldehyde to a carboxylic acid). If the...
- Determine No. Of Structural Isomers
← Back to Intro to Org Chem [Bad News] There is no mathematical formula available to calculate the number of structural isomers. You have to draw out all possible structures. [Good News] There is a general approach for that. ...
- H1 Chemistry Syllabus (2008)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND STOICHIOMETRY • Relative masses of atoms and molecules • The mole, the Avogadro constant • The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae • Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases) 2....
